Lab 2 Overview
As we saw earlier, the sample application is a three-tiered application –> frontend, backend, database.
For our lab, another version of the application exists that breaks out each of these backend services into separate services. By putting these services into Docker images, we gain the ability to deploy the service into modern platforms like Kubernetes and AWS services such as the ones shown below.

Kubernetes
Kubernetes is open source software that allows you to deploy and manage containerized applications at scale.
Kubernetes manages clusters of compute instances and runs containers on those instances with processes for deployment, maintenance, and scaling. Using Kubernetes, you can run any type of containerized applications using the same toolset on-premises and in the cloud.
You can read more about Kubernetes here
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service
AWS makes it easy to run Kubernetes. You can choose to manage Kubernetes infrastructure yourself with Amazon EC2 or get an automatically provisioned, managed Kubernetes control plane with Amazon EKS. Either way, you get powerful, community-backed integrations to AWS services like VPC, IAM, and service discovery as well as the security, scalability, and high-availability of AWS.
Amazon EKS runs Kubernetes control plane instances across multiple Availability Zones to ensure high availability. Amazon EKS automatically detects and replaces unhealthy control plane instances, and it provides automated version upgrades and patching for them.
Amazon EKS is also integrated with many AWS services to provide scalability and security for your applications, including the following:
- Elastic Load Balancing for load distribution
- IAM for authentication
- Amazon VPC for isolation
- Amazon ECR for container images
For this workshop you are going to use Amazon EKS managed service that makes it easy for you to run Kubernetes on AWS without needing to stand up or maintain your own Kubernetes control plane.
Lab Setup
Refer to the picture below, here are the components for lab 2.

#1 . Sample Application Sample app representing a “services” architecture of a frontend and multiple backend services implemented as Docker containers that we will review in this lab.
#2 . Kubernetes Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) is hosting the application. The Kubernetes cluster had the Dynatrace OneAgent Operator installed. (see below for more details). Two EKS nodes make up the Kubernetes cluster. The Dynatrace OneAgent was preinstalled by the OneAgent operator and is sending data to your Dynatrace SaaS environment. (see below for more details)
#3 . Dynatrace Operator Dynatrace OneAgent is container-aware and comes with built-in support for out-of-the-box monitoring of Kubernetes. Dynatrace supports full-stack monitoring for Kubernetes, from the application down to the infrastructure layer.
#4 . Dynatrace Dynatrace tenant where monitoring data is collected and analyzed.
#5 . Full-Stack Dashboard Made possible by the Dynatrace OneAgent that will automatically instrument each running node & pod in EKS.
#6 . Kubernetes Dashboard The Kubernetes page provides an overview of all Kubernetes clusters showing monitoring data like the clusters’ sizing and utilization.
Beyond the Lab
Over time, you can imagine that this sample application will be further changed to add in other technologies like AWS Lambda functions and other PaaS services like AWS RDS or Aurora databases and virtual networking Application gateways as shown in the picture below.
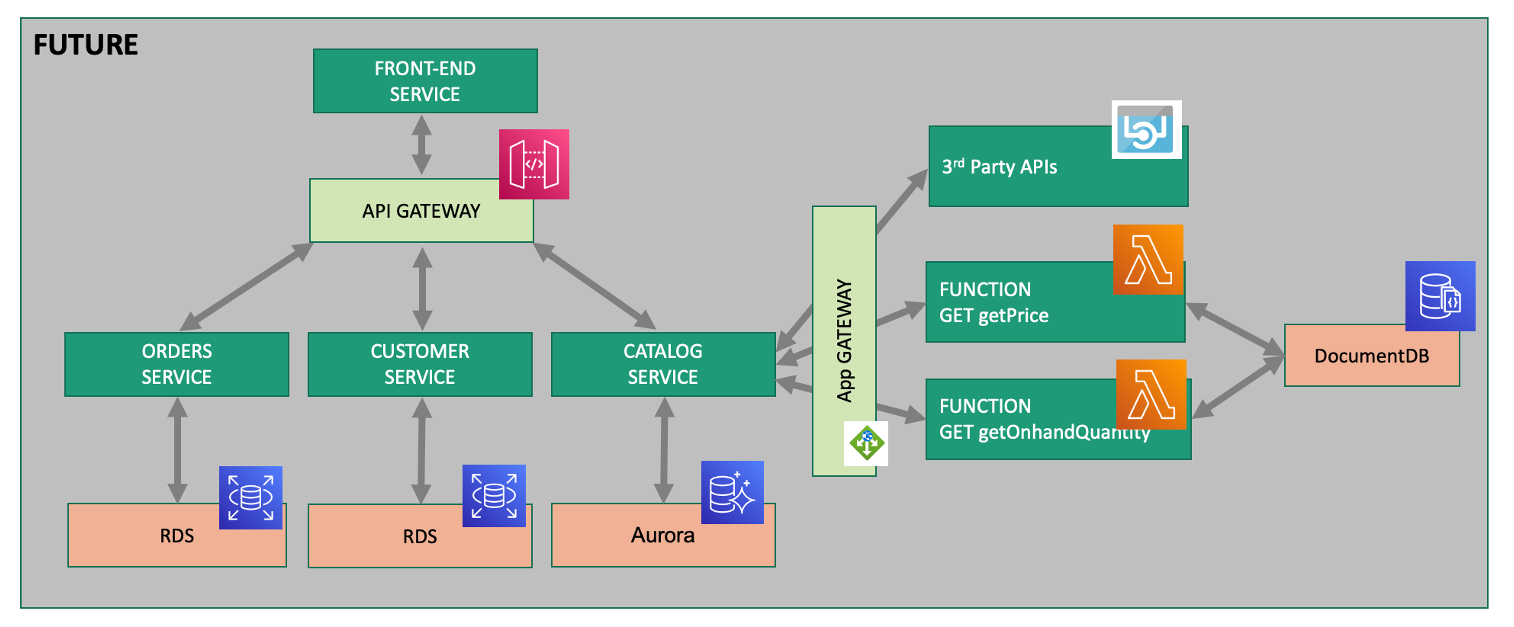
💥 TECHNICAL NOTE
We will not cover this, but organizations are establishing DevOps approaches and Continuous Integration (CI) pipelines to build and test each service independently. They are also adding Continuous Deployment (CD) as well to the process too that vastly increases our ability to delivery features faster to our customers.