What is AWS Lambda?
What is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda functions are a good example of how a serverless framework works:
- Developers write a function in a supported language or platform.
- The developer uploads the function and configuration for how to run the function to the cloud.
- The platform handling the function containerizes it.
- The platform builds the trigger to initiate the app.
- Every time the trigger executes, the function runs on an available resource.
- When an application is triggered, it can cause latency as the application sometimes will cold start.
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that runs your code in response to events and automatically manages the underlying compute resources for you. These events may include changes in state or an update, such as a user placing an item in a shopping cart on an ecommerce website. You can use AWS Lambda to extend other AWS services with custom logic, or create your own backend services that operate at AWS scale, performance, and security. AWS Lambda automatically runs code in response to multiple events, such as HTTP requests via Amazon API Gateway, modifications to objects in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets, table updates in Amazon DynamoDB, and state transitions in AWS Step Functions.
It also runs your code on high availability compute infrastructure and performs all the administration of your compute resources. This includes server and operating system maintenance, capacity provisioning and automatic scaling, code and security patch deployment, and code monitoring and logging. All you need to do is supply the code.
The Lambda Architecture?
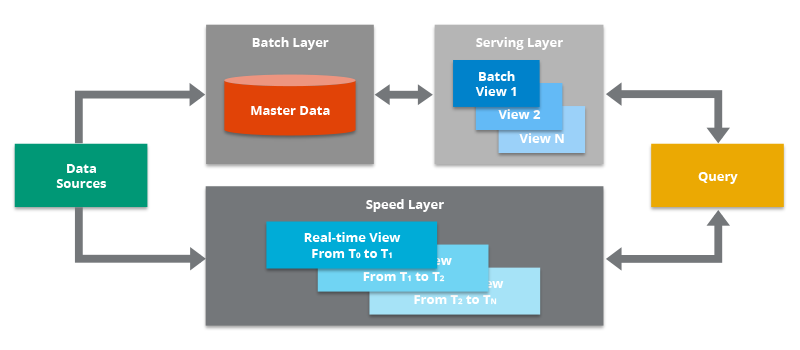
Lambda architecture is a data deployment model for processing that consists of a traditional batch data pipeline and a fast streaming data pipeline for handling real-time data. In addition to the batch layer and speed layers, Lambda architecture also includes a data serving layer for responding to user queries.
The Lambda A-Typical Usecases
-
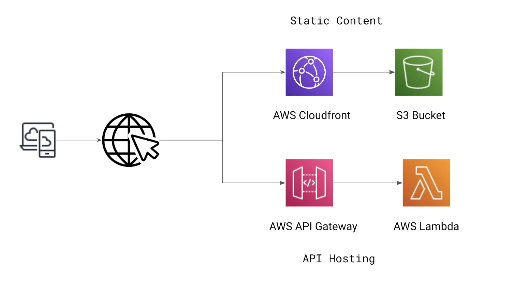
Suppose you are creating a website and you want to host the backend logic on Lambda. You can invoke your Lambda function over HTTP using Amazon API Gateway as the HTTP endpoint. Now, your web client can invoke the API, and then API Gateway can route the request to Lambda.
-
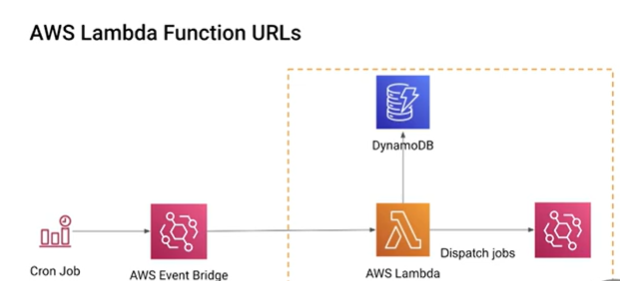
Lambda is great for running repetitive tasks such as cronjobs
-
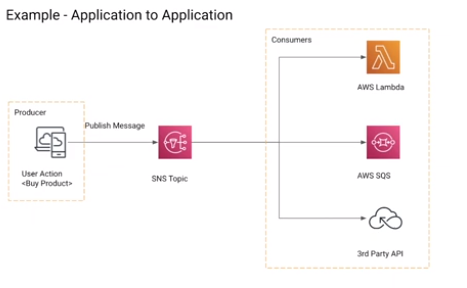
Another popular use case is events processing When working with stream-based event sources, you create event source mappings in AWS Lambda. Lambda reads items from the stream and invokes the function synchronously.
-
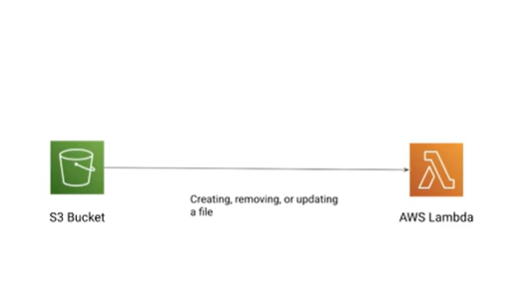
Suppose you have a photo sharing application. People use your application to upload photos, and the application stores these user photos in an Amazon S3 bucket. Then, your application creates a thumbnail version of each user’s photos and displays them on the user’s profile page. In this scenario, you may choose to create a Lambda function that creates a thumbnail automatically. Amazon S3 is one of the supported AWS event sources that can publish object-created events and invoke your Lambda function. Your Lambda function code can read the photo object from the S3 bucket, create a thumbnail version, and then save it in another S3
-
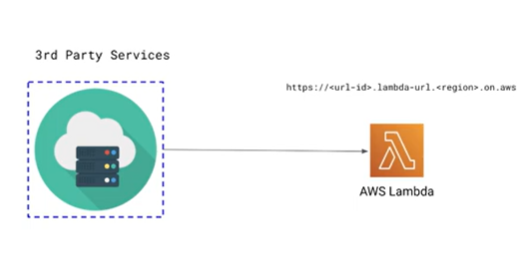
Last but certainly not final is managing webhooks as our applications rely on 3rd party services. Lambda in this case is used to manage the conneciton of the webhook to the serivces and freeing from managing this vm or other hardware to run this.