Custom Alerting
Dynatrace Davis automatically analyzes abnormal situations within your IT infrastructure and attempts to identify any relevant impact and root cause. Davis relies on a wide spectrum of information sources, such as a transactional view of your services and applications, as well as all on events raised on individual nodes within your Smartscape topology.
There are two main sources for single events in Dynatrace:
- Metric-based events (events that are triggered by a series of measurements)
- Events that are independent of any metric (for example, process crashes, deployment changes, and VM motion events)
Custom metric events are configured in the global settings of your environment and are visible to all Dynatrace users in your environment.
1. Setup Custom metric alerting for AWS
1 . To add custom alerts, navigate to Settings --> Anomaly Detection --> Custom Events for Alerting menu.
2 . Click the Create custom event for alerting button.

3 . In the Metric dropdown list, type EC2 CPU usage % and pick the Cloud platforms > AWS > EC2 > CPU > usage option and Pick Average
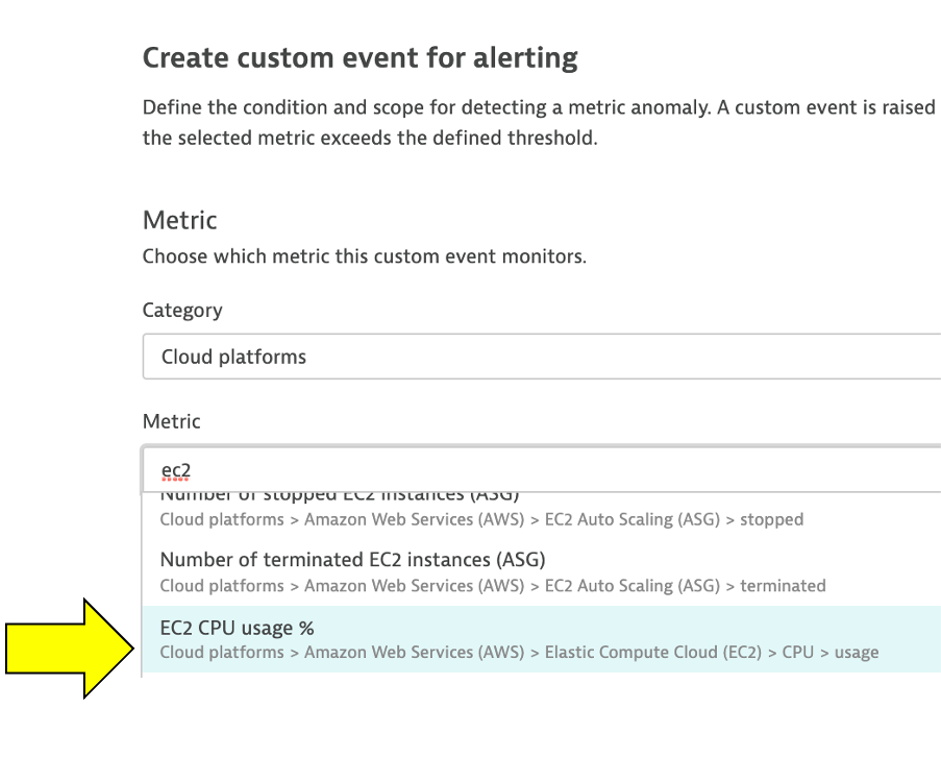
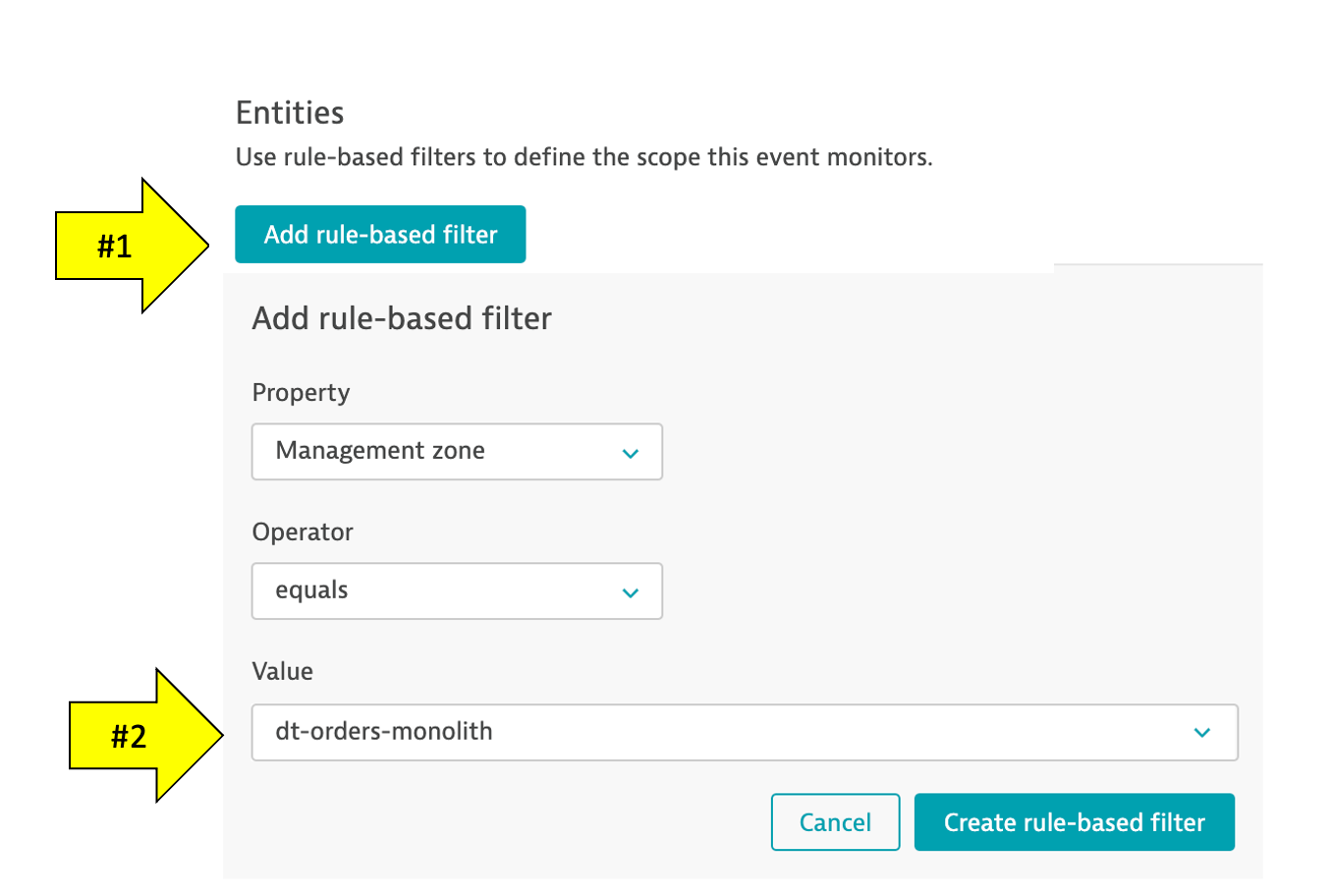
4 . Click Add rule-base button and update as shown below
5 . Choose Static threshold and update as shown below

6 . Add the Event Description to have the title and severity = CUSTOM ALERT as shown below.
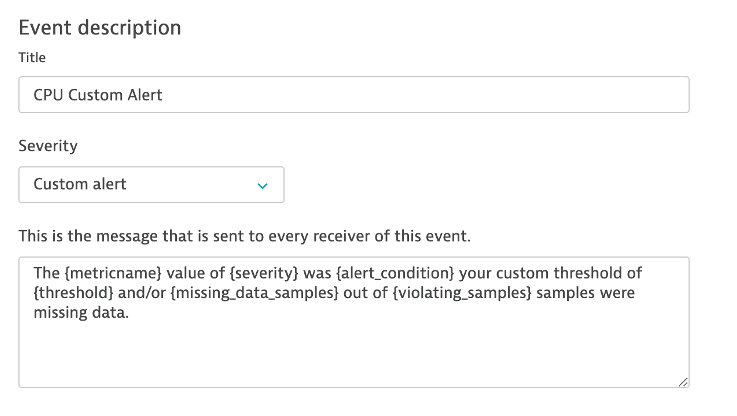
Notice the Alert preview chart that helps you in reviewing these settings

7 . Save your changes
8 . Add another rule, with everything the same, except for the Event Description to have the title and severity = RESOURCE as shown below.

9 . Save your changes and the list should look as shown below.

2. SSH to monolith host
Run this command to get the command to SSH into the monolith host.
cd ~/aws-modernization-dt-orders-setup/learner-scripts/
./show-app-urls.shFrom the output you should see a command like ssh -i "~/aws-modernization-dt-orders-setup/gen/<YOUR-LASTNAME>-dynatrace-modernize-workshop.pem" ubuntu@11.22.33.44
Copy and paste that command to SSH to the monolith VM. You should see output like this and b e presented another command prompt.
Welcome to Ubuntu 18.04.4 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.15.0-1065-aws x86_64)
...
...
To run a command as administrator (user "root"), use "sudo <command>".
See "man sudo_root" for details.
ubuntu@ip-10-0-0-118:~$ 3. Trigger a CPU problem
In the shell, copy all these lines and run them:
yes > /dev/null &
yes > /dev/null &
yes > /dev/null &To verify, run this command:
ps -ef | grep yesThe output should look like this:
ubuntu 5802 5438 99 20:48 pts/0 00:00:05 yes
ubuntu 5805 5438 89 20:48 pts/0 00:00:04 yes
ubuntu 5806 5438 97 20:48 pts/0 00:00:03 yes
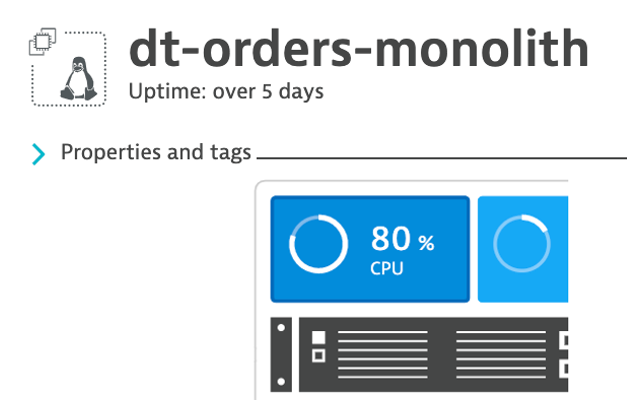
ubuntu 5818 5438 0 20:48 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto yes3 . Back in Dynatrace within the host view, the CPU should now be high as shown below
4 . It may take a minute or so, but you will get two problem cards as shown below. #1 is the alert from the severity = RESOURCE where Davis was invoked, and #2 is the alert from severity = CUSTOM ALERT.

4. Review Problem Notifications
1 . Navigate to Settings --> Integrations --> Problem Notifications
2 . Read the overview and then click the Add Notification button
3 . Click various Notification types from the drop down to review the configurations inputs.
4 . For the Custom integration type, review the option to customize the payload.
5 . Notice how you can choose the Alert profile, but you only have default
5. Review Alerting Profiles
1 . Navigate to Settings --> Alerting --> Alerting profiles
2 . Read the overview and then expand the default rule.
3 . Now add one, by clicking on the Add alerting profile button
4 . Review the options to choose severity rules and filters
6. Stop the CPU problem
To stop the problem, you need to kill the processes. To do this:
1 . Back in the CloudShell, run this command to get the process IDs ps -ef | grep yes
2 . For each process, copy the process ID and run kill <PID>
For example:
# If output is this...
ubuntu@ip-10-0-0-118:~$ ps -ef | grep yes
ubuntu 5802 5438 99 20:48 pts/0 00:00:05 yes
ubuntu 5805 5438 89 20:48 pts/0 00:00:04 yes
ubuntu 5806 5438 97 20:48 pts/0 00:00:03 yes
# Then run...
kill 5802
kill 5805
kill 58063 . Verify they are gone by running this again ps -ef | grep yes
4 . Verify that CPU in Dynatrace goes to normal and the problems will eventually automatically close
6. Exit the SSH
Simply type exit to exit the VM and return the CloudShell.
💥 TECHNICAL NOTE
See the Dynatrace Docs for more details on the setup.
Alert configuration is available through the Anomaly detection—metric events API. Using the API, you can list, update, create, and delete configurations.